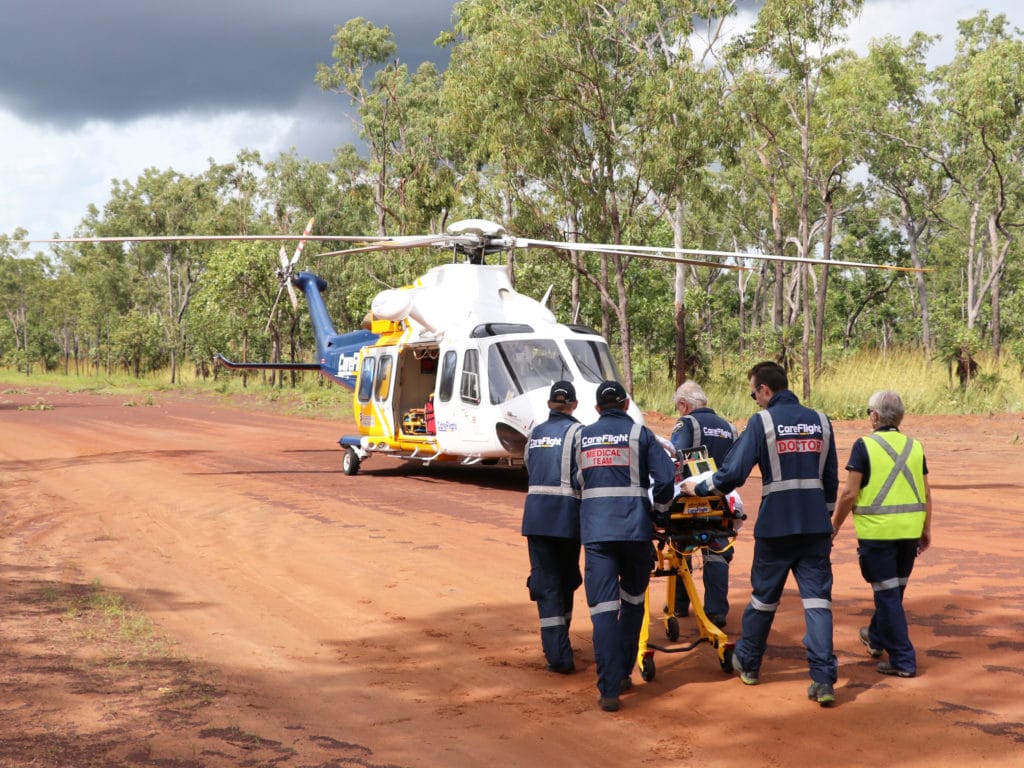
Imagine this scenario: You’re in a remote area, far away from the nearest hospital, and suddenly someone experiences a life-threatening medical emergency. Time is of the essence, and traditional modes of transportation are simply too slow to get the person the help they urgently need. This is where air ambulances come to the rescue. These specialized aircraft, equipped with state-of-the-art medical equipment and staffed by highly trained professionals, provide a lifeline to those in remote areas who require immediate medical attention. In this article, we will explore how air ambulances save lives in these hard-to-reach locations, delving into the critical role they play in ensuring timely and efficient emergency medical care.

How Air Ambulances Save Lives in Remote Areas
When it comes to medical emergencies, time is of the essence. In remote areas where access to medical facilities is limited and geographical barriers pose significant challenges, air ambulances play a vital role in saving lives. In this article, we will explore the definition, purpose, and different types of air ambulances, as well as the training and certification required for their operations.
1. Introduction to Air Ambulances
1.1 Definition and Purpose
Air ambulances, also known as medical helicopters or aeromedical services, are specialized aircraft specifically designed and equipped to facilitate the transportation of critically ill or injured patients. Their primary purpose is to provide rapid medical response and transport individuals in need of urgent medical care to healthcare facilities that are often located far away.
1.2 Types of Air Ambulances
There are two main types of air ambulances: helicopter-based and fixed-wing aircraft. Helicopter-based air ambulances are typically used for shorter distances and quick response times, while fixed-wing aircraft are better suited for longer distances and interfacility transfers. Both types are equipped with medical equipment and staffed by highly trained medical professionals.
1.3 Training and Certification
The crew aboard air ambulances consists of highly skilled medical personnel, including paramedics, nurses, and physicians. These individuals undergo specialized training and certification to ensure they can provide optimal care to patients during transportation. Training programs cover a wide range of topics, including aviation safety, medical procedures, and emergency management, to guarantee the highest level of competence and expertise.
2. Challenges in Remote Areas
2.1 Limited Access to Medical Facilities
One of the primary challenges faced in remote areas is the limited access to medical facilities. People living in remote regions often have to travel long distances to receive adequate medical care. This lack of accessibility can result in delays in treatment, worsening of medical conditions, and even fatalities. Air ambulances help bridge this gap by providing rapid transportation to healthcare facilities, ensuring patients receive timely and critical care.
2.2 Geographical Barriers
Remote areas are often characterized by challenging geographical barriers, such as mountains, dense forests, or vast water bodies. These barriers can hinder ground transportation, making it difficult for traditional ambulances to reach individuals in need. Air ambulances are essential in such situations as they can navigate through challenging terrain and reach patients swiftly, bypassing these geographical obstacles.
2.3 Time Sensitivity
During medical emergencies, time plays a crucial role in determining the outcome for patients. In remote areas, where medical facilities are scarce, timely access to specialized care can mean the difference between life and death. Air ambulances are equipped to land directly at the scene of an emergency, allowing for rapid assessment, stabilization, and transport of patients to healthcare facilities. The time-sensitive nature of these services significantly improves the chances of survival and better patient outcomes.

3. Role of Air Ambulances in Remote Areas
3.1 Speed and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of air ambulances in remote areas is their speed and efficiency. Unlike ground transportation, air ambulances can cover vast distances in a relatively short amount of time. This swift response enables medical professionals to reach patients quickly, provide initial treatment at the scene, and transport them to appropriate healthcare facilities without delays caused by traffic or challenging terrain.
3.2 Critical Care Services
Air ambulances are equipped with state-of-the-art medical equipment and staffed by highly trained professionals capable of delivering critical care services. These advanced medical capabilities enable air ambulances to provide a higher level of care compared to traditional ambulances. The availability of specialized medical procedures, such as advanced life support, monitoring, and diagnostic tools, ensures that patients receive the necessary treatment during transport, further increasing their chances of survival.
3.3 Accessible Transportation
For patients in remote areas, reaching a medical facility can be a daunting task. The lack of accessible transportation options can lead to delays in receiving medical care and potentially worsen their condition. Air ambulances offer a solution to this problem by providing accessible transportation directly from the scene of the emergency to the nearest appropriate healthcare facility. This streamlined approach ensures that patients’ medical needs are met promptly and efficiently.
3.4 Helipads and Landing Zones
To facilitate the operations of air ambulances in remote areas, the presence of helipads and landing zones is crucial. These designated areas allow helicopter-based air ambulances to safely land and take off, even in areas with challenging terrain. Building and maintaining these helipads and landing zones in remote regions can significantly improve the access and availability of air ambulances, ensuring prompt and effective care for patients in need.
4. Medical Equipment and Capabilities
4.1 Advanced Life Support
Air ambulances are equipped with advanced life support equipment that enables medical professionals to provide immediate medical interventions to critically ill or injured patients. This includes equipment for airway management, cardiac monitoring, defibrillation, and administration of life-saving medications. The presence of these advanced medical capabilities ensures that patients receive the necessary interventions to stabilize their condition during transport.
4.2 Monitoring and Diagnostic Tools
In addition to advanced life support equipment, air ambulances also possess a wide range of monitoring and diagnostic tools. These tools allow medical professionals to continuously assess the patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate, during transport. This real-time monitoring helps detect any changes or complications promptly, enabling the medical team to intervene as necessary and provide appropriate care.
4.3 Ventilation and Oxygen Support
Air ambulances are equipped with ventilation and oxygen support systems to provide respiratory support to patients who may have difficulty breathing on their own or require supplemental oxygen. These systems ensure that patients with compromised respiratory function receive the necessary support to maintain adequate oxygenation and ventilation throughout the transport process.
4.4 Medications and Blood Products
To address the medical needs of patients during transport, air ambulances are equipped with a wide range of medications and blood products. These include pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and anticoagulants, among others. The availability of these medications and blood products ensures that patients receive appropriate treatment for their underlying conditions or any emergent medical needs that may arise during transport.
5. Patient Stabilization and Transport
5.1 Pre-Hospital Stabilization
Before embarking on the transport, air ambulance teams are trained to provide accurate and effective pre-hospital stabilization. This involves assessing and managing the patient’s condition at the scene of the emergency, initiating necessary interventions to stabilize vital signs and prevent further deterioration. The goal is to optimize the patient’s condition for safe transport to a healthcare facility while minimizing potential complications during the journey.
5.2 Safe Transfer and Transport
The safe transfer and transport of patients are of utmost importance in air ambulance operations. The medical crew ensures that patients are securely strapped in, utilizing appropriate restraints and harnesses to prevent any movement or injury during travel. Additionally, the aircraft is equipped with specialized medical beds or stretchers that provide comfort and support to patients during the journey.
5.3 Continuous Medical Monitoring
Throughout the entire transport process, air ambulances provide continuous medical monitoring to ensure the stability and well-being of the patient. This includes ongoing assessment of vital signs, monitoring of medical equipment and interventions, and close observation of any changes or complications that may arise. The medical team remains vigilant and ready to address any medical emergencies that may occur during transport.
6. Coordination with Ground Medical Teams
6.1 Dispatch and Communication
Effective coordination between air ambulances and ground medical teams is essential for seamless patient care. Dispatch centers receive calls for medical emergencies and initiate the deployment of air ambulances as required. Constant communication between the air ambulance crew, dispatch, and ground medical teams ensures that the transport process is well-coordinated and that the receiving healthcare facility is prepared to receive the patient upon arrival.
6.2 Medical Consultations
During transport, air ambulance crews can maintain communication with medical professionals at receiving healthcare facilities. This allows for medical consultations and the exchange of critical information regarding the patient’s condition, medical history, and required interventions. The ability to consult and collaborate with healthcare professionals en route enhances the provision of appropriate and timely care for the patient.
6.3 Handover and Transfer of Care
Upon arrival at the receiving healthcare facility, a seamless handover and transfer of care take place. The air ambulance team provides detailed information about the patient’s condition, interventions performed during transport, and any changes or complications observed. This comprehensive handover ensures continuity of care, allowing the medical staff at the receiving facility to continue providing appropriate treatment without delay.
7. Weather and Navigation Considerations
7.1 Weather-Based Limitations
Weather conditions can significantly impact air ambulance operations, especially in remote areas. Severe weather, such as thunderstorms, high winds, or heavy fog, may limit or even prevent the safe operation of air ambulances. Pilots are trained to closely monitor weather patterns and make informed decisions regarding flight safety. This consideration ensures that both the medical crew and patient remain safe during transport.
7.2 Navigation Systems and Expertise
Air ambulances are equipped with advanced navigation systems that assist pilots in navigating through remote and challenging terrain. These systems, including GPS and other navigational aids, provide real-time information about the aircraft’s position, altitude, and flight path. Pilots, along with their experience and expertise, rely on these navigation systems to ensure safe and efficient transport, even in areas with limited ground-based navigation aids.
8. Medical Crew and Expertise
8.1 Roles and Responsibilities
The medical crew aboard air ambulances consists of highly trained professionals with specific roles and responsibilities. Paramedics, nurses, and physicians work together as a cohesive team to provide optimal care to patients during transport. Paramedics are responsible for initial patient assessment, stabilization, and emergency interventions. Nurses provide ongoing care, medication administration, and communication with the receiving facility. Physicians oversee the medical management and decision-making process, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate level of care for their condition.
8.2 Medical Training and Experience
Each member of the medical crew undergoes extensive training and possesses a high level of medical expertise. Paramedics and nurses receive specialized training in critical care and emergency medicine, enabling them to care for patients with complex medical conditions. Physicians onboard air ambulances have additional training, such as in emergency medicine or critical care, and bring a wealth of clinical experience to the team. This collective expertise ensures that patients receive the highest standard of care during transport.
8.3 Team Dynamics
Effective teamwork and communication are crucial elements of air ambulance operations. The medical crew aboard air ambulances undergo team training exercises to enhance their ability to work cohesively and efficiently. These exercises focus on effective communication, task delegation, and mutual support during high-stress situations. The seamless coordination and collaboration among the medical crew contribute to the safe and successful transport of patients in remote areas.
9. Cost and Affordability
9.1 Insurance Coverage
The cost of air ambulance services can be a concern for individuals requiring urgent medical transport in remote areas. Insurance coverage plays a vital role in making these services more affordable for patients. Many insurance providers offer coverage for air ambulance transportation, allowing individuals to access this critical service without incurring significant financial burdens. It is essential to review insurance policies and understand coverage options to ensure adequate protection during medical emergencies.
9.2 Government Funding
In some cases, government funding is available to support air ambulance services in remote areas. Governments understand the importance of providing timely medical care to individuals residing in these underserved regions. Subsidies or grants may be provided to air ambulance operators, helping to offset operational costs and ensure the ongoing availability of these life-saving services.
9.3 Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations also play a significant role in supporting air ambulance services in remote areas. These organizations rely on donations and fundraising initiatives to finance their operations. By partnering with local communities and leveraging charitable contributions, non-profit organizations can provide air ambulance services at reduced or no cost to individuals in need.
9.4 Medical Evacuation Membership Programs
Medical evacuation membership programs offer individuals the opportunity to access air ambulance services at a discounted rate. By paying a membership fee, individuals become eligible for reduced out-of-pocket costs associated with air ambulance transport. These programs are particularly beneficial for individuals living in remote areas, as they provide peace of mind and financial protection in the event of a medical emergency.
In conclusion, air ambulances have revolutionized the way medical emergencies are managed in remote areas. Their speed, efficiency, and advanced medical capabilities allow for prompt and effective care, resulting in improved patient outcomes. By overcoming the challenges of limited access to medical facilities and geographical barriers, air ambulances save lives by providing timely and critical care to those who need it most.