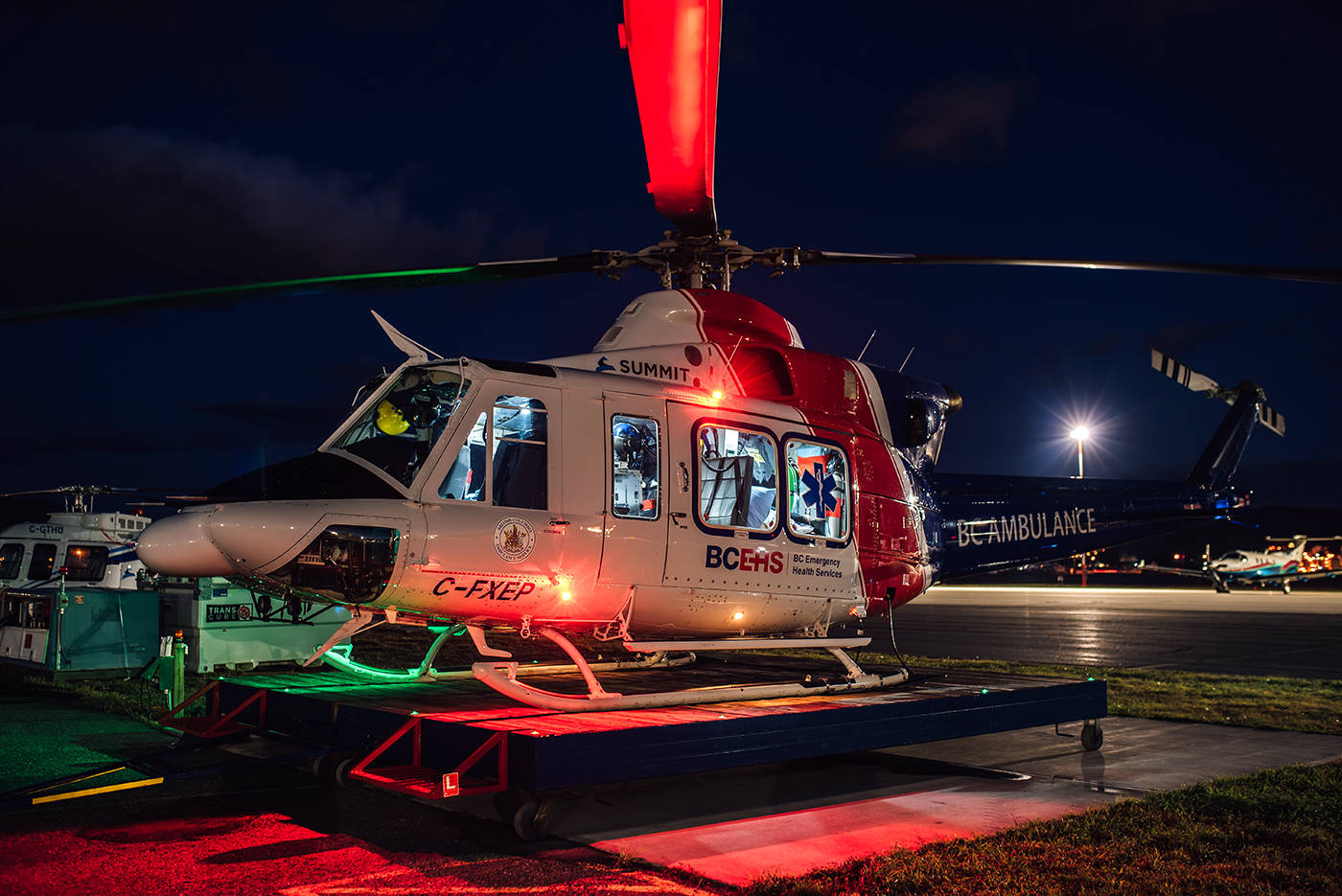
Picture this: it’s the dead of night, the stars are sparkling brightly overhead, and in the distance, you hear the distinct sound of a helicopter rotor spinning. That’s right, it’s an air ambulance making its way through the darkness, on a mission to save lives. But have you ever wondered how these incredible aircraft navigate in the dark? How do they ensure they reach their destination safely and swiftly, even when visibility is limited? In this article, we’ll shed some light on the fascinating world of nighttime operations for air ambulances. Get ready to discover the secrets behind their navigation techniques and the cutting-edge technology that enables them to soar through the night sky with precision and care. Let’s dive right in!

1. Importance of Nighttime Operations
Nighttime operations play a crucial role in the effectiveness and efficiency of air ambulance services. The cover of darkness brings unique challenges, but it also presents opportunities to enhance accessibility, respond to urgent medical situations, reduce traffic congestion, and ensure efficient patient transportation.
1.1 Enhanced Accessibility
In emergency situations, every minute counts. Nighttime operations enable air ambulances to reach remote or hard-to-access locations more quickly and efficiently. This can make a significant difference in critical medical cases where time is of the essence. By leveraging advanced technology and expertise, air ambulances can navigate through the darkness, overcoming obstacles that might hinder ground transportation.
1.2 Urgent Medical Situations
Medical emergencies don’t wait for daylight, and neither should the response. Air ambulances equipped for nighttime operations can swiftly transport patients to specialized medical facilities during the critical golden hour. Prompt medical attention in such cases dramatically increases the chances of survival and recovery. Whether it’s a heart attack, stroke, or trauma, the ability to operate at night ensures that patients receive immediate and lifesaving care.
1.3 Reduced Traffic Congestion
The cover of darkness brings about reduced traffic congestion on both roads and in the airspace. This advantage allows air ambulances to navigate more freely and efficiently, saving valuable time during transit. By bypassing traffic congestion, air ambulances can quickly transport patients without being hindered by the limitations of ground transportation. This is particularly beneficial in urban areas where traffic congestion can significantly delay medical response times.
1.4 Efficient Patient Transportation
Nighttime operations offer air ambulances the ability to efficiently transport patients over long distances, especially in situations where ground transportation may not be feasible or timely. With the aid of advanced aviation technology and flight planning, air ambulances can optimize routing, ensuring the fastest and smoothest journey for patients. This increased efficiency allows medical teams to reach their destinations and initiate appropriate treatment promptly.
2. Night Vision Devices
To safely navigate through the darkness, air ambulances rely on several advanced night vision devices. These cutting-edge technologies enable flight crews to overcome the challenges posed by limited visibility and perform their lifesaving missions effectively.
2.1 Night Vision Goggles (NVGs)
One of the most critical tools in nighttime operations is the use of Night Vision Goggles (NVGs). These specially designed goggles amplify the available light, enabling flight crews to see clearly in near-total darkness. NVGs enhance visibility, allowing pilots to identify hazards, obstacles, and landmarks that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye. With the aid of NVGs, air ambulances can operate safely and confidently even in the darkest of nights.
2.2 Forward-Looking Infrared (FLIR) Systems
Forward-Looking Infrared (FLIR) systems are another invaluable technology utilized in air ambulance nighttime operations. FLIR systems detect and display thermal radiation, converting it into a visible image for the flight crew. This allows them to identify heat signatures, such as humans, animals, or vehicle engines, even in complete darkness. By providing enhanced situational awareness, FLIR systems help air ambulances avoid potential obstacles and ensure a safe journey for patients.
2.3 Infrared Illumination
Infrared Illumination is a method of providing additional lighting for night operations. By emitting infrared light that is invisible to the naked eye but visible through night vision devices, air ambulances can illuminate landing zones, helipads, or other critical areas. This ensures that flight crews have sufficient visibility during takeoff, landing, and ground operations. Infrared Illumination helps mitigate the risks associated with limited visibility and enhances overall safety during nighttime operations.
2.4 Cockpit Lighting Modifications
To optimize visibility and ensure the efficient operation of flight instruments during nighttime missions, air ambulances often make specific cockpit lighting modifications. These modifications aim to minimize glare, increase contrast, and improve the readability of critical instruments and displays. By customizing cockpit lighting to suit nighttime operations, flight crews can maintain situational awareness and safely execute their missions, regardless of the time on the clock.

3. Flight Planning and Instrumentation
Successful nighttime operations require meticulous flight planning and the use of appropriate instrumentation. This ensures that air ambulances can safely navigate through the darkness and reach their destinations without compromising patient care.
3.1 Weather Considerations
When planning nighttime missions, air ambulance crews must consider a range of weather factors that can impact flight safety. This includes visibility, cloud cover, winds, and potential weather hazards such as thunderstorms or icing. By closely monitoring weather conditions and utilizing real-time weather updates, air ambulances can make informed decisions about flight routes and take necessary precautions to ensure the safety of the crew, patients, and aircraft.
3.2 Obstacle Avoidance Systems
To mitigate the risks posed by obstacles during nighttime operations, air ambulances are equipped with advanced obstacle avoidance systems. These systems rely on a combination of technology, such as radar, GPS, and terrain databases, to detect and warn flight crews about potential obstacles such as buildings, towers, or mountains. By incorporating these systems into flight planning and navigation, air ambulances can navigate safely even during the darkest nights.
3.3 GPS Navigation Systems
GPS navigation systems are vital tools in modern air ambulances, providing accurate and real-time information about the aircraft’s position, speed, and direction of travel. During nighttime operations, GPS navigation systems ensure precise navigation, enabling flight crews to follow planned routes and avoid unauthorized airspace. This technology minimizes the risk of spatial disorientation and enhances the safety of the crew, patients, and the aircraft.
3.4 Instrument Flight Rules (IFR)
Air ambulances operating at night typically utilize Instrument Flight Rules (IFR), which provide standardized procedures and regulations for flying in low visibility conditions. By adhering to IFR procedures, flight crews rely on flight instruments and ground-based navigation aids to navigate through the darkness. This ensures precise navigation, aids in obstacle avoidance, and enhances overall flight safety.
4. Air Traffic Control and Communication
Coordinated communication and interaction with air traffic control are essential elements of nighttime operations for air ambulances. These protocols ensure the safe and efficient movement of the aircraft and facilitate seamless coordination with ground crews.
4.1 Coordination with Air Traffic Control
Air ambulances operating at night follow specific communication and coordination protocols with air traffic control. This includes obtaining clearances for departure, arrival, and any required deviations from planned routes. By maintaining open lines of communication with air traffic control, air ambulances can avoid potential conflicts with other aircraft and ensure a smooth and safe transit to their destination.
4.2 Frequent Communication Updates
During nighttime operations, air ambulances maintain frequent communication updates with air traffic control to address changes in weather conditions, flight plans, or emergency situations. Prompt and clear communication allows air traffic control to provide necessary guidance and ensure the safety of the aircraft. These frequent updates facilitate real-time decision-making and mitigate risks associated with nighttime operations.
4.3 Emergency Radio Frequencies
Nighttime operations demand heightened awareness of emergency radio frequencies. By monitoring designated emergency frequencies, air ambulances can quickly communicate distress calls or request assistance in critical situations. This seamless communication ensures rapid response times and reinforces the safety and effectiveness of nighttime air ambulance operations.
4.4 Two-Way Radio Protocols
Two-way radio protocols are essential for effective communication between air ambulances and air traffic control, as well as ground crews. By adhering to established two-way radio protocols, flight crews can ensure clear and concise communication, even in stressful or challenging nighttime situations. These protocols improve overall coordination, minimize misunderstandings, and maintain a safe operating environment.

5. Crew Training and Expertise
To navigate the unique challenges of nighttime operations, air ambulance crews undergo specialized training and acquire the necessary expertise. This comprehensive training equips them to make critical decisions, safely navigate through the darkness, and respond effectively to emergencies.
5.1 Nighttime Flight Simulation
Flight simulation programs play a critical role in training air ambulance crews for nighttime operations. These simulations accurately replicate the challenges and scenarios encountered during nighttime missions, allowing crews to practice flight maneuvers, navigation, and emergency procedures. By providing a realistic training environment, nighttime flight simulation enhances crew preparedness and decision-making abilities in the face of adversity.
5.2 Nighttime Decision-Making Training
Nighttime operations demand quick and accurate decision-making skills from air ambulance crews. Specialized training programs focus on developing these vital skills, ensuring that crews can assess risks, adapt to changing circumstances, and prioritize patient care during nighttime operations. This training emphasizes the importance of remaining calm, using available resources effectively, and making well-informed decisions under time pressure.
5.3 Specialized Nighttime Navigation Training
Air ambulance crews receive specialized training in nighttime navigation techniques to safely operate in low visibility conditions. This training includes understanding the use of night vision devices, interpreting cockpit instrumentation, and utilizing GPS navigation systems effectively. By mastering these navigation techniques, air ambulance crews can confidently navigate through the darkness, avoiding hazards and ensuring smooth patient transportation.
5.4 Emergency Procedures Preparation
The ability to respond effectively to emergencies is a core component of air ambulance crew training. Nighttime operations introduce unique challenges that require crews to be prepared for any scenario that may arise. Specialized training prepares crews to handle emergencies such as equipment malfunctions, rapid weather changes, or inflight medical incidents. Through regular drills and simulations, air ambulance crews develop muscle memory and confidence in their ability to mitigate risks and protect the well-being of patients.
6. Lighting and Markings on Air Ambulances
Proper lighting and markings on air ambulances are essential for safe operations during nighttime missions. These considerations not only aid in visibility but also help identify and distinguish air ambulances from other aircraft.
6.1 High-Visibility Exterior Lighting
Air ambulances are equipped with high-visibility exterior lighting systems to ensure optimal visibility during nighttime operations. These lighting systems typically include powerful searchlights, anti-collision strobe lights, and navigation lights. The combination of these lights helps other aircraft, ground crews, and those on the ground to easily identify and track the movement of air ambulances during nighttime emergencies.
6.2 Aircraft Identification Markings
Distinctive markings and color schemes are applied to air ambulances to facilitate quick and accurate identification, especially during nighttime operations. These markings might include prominent logos, medical symbols, or high-contrast color schemes that improve the visibility and recognition of air ambulances both in the air and on the ground. Clear identification markings enable efficient coordination between air and ground crews, streamlining the overall operation and ensuring accurate patient transportation.
6.3 Helipad Lighting Requirements
Helipad lighting is an essential component of nighttime air ambulance operations, ensuring safe takeoff and landing procedures. Adequate helipad lighting includes perimeter lights, approach and threshold lights, and floodlights to illuminate the touchdown area. By following established helipad lighting requirements, air ambulances can safely navigate to and from the helipad, minimizing the risk of accidents during takeoff and landing.
6.4 Cabin Lighting Considerations
Proper cabin lighting is crucial for providing a safe and comfortable environment for patients during nighttime air ambulance operations. Cabin lighting should be adjustable to ensure appropriate levels of brightness for medical procedures, assessment, and stabilization. Additionally, cabin lighting should not interfere with the flight crew’s vision or disrupt nighttime visual cues. By optimizing cabin lighting, air ambulances can provide optimal conditions for patient care while maintaining the safety and efficacy of the nighttime operation.

7. Collaborative Operations with Ground Crew
Successful nighttime air ambulance operations heavily rely on collaboration and coordination with ground crews. This requires effective communication and proactive planning to ensure seamless transitions between air and ground transportation.
7.1 Ground Transport Coordination
Air ambulances must collaborate closely with ground transportation teams to ensure the smooth transfer of patients. This coordination involves efficient communication regarding patient information, location details, and anticipated arrival times. Ground transport coordination considers factors such as traffic conditions, road closures, and any potential obstacles that might impact the patient’s journey from the aircraft to the receiving medical facility. By working together, air and ground crews can minimize transfer times and ensure the continuity of patient care.
7.2 Landing Zone Preparation
Ground crews play a vital role in preparing suitable landing zones for air ambulance arrivals and departures. This includes securing the landing area, removing any potential hazards, and ensuring adequate lighting and ground markings to aid the flight crew’s visibility. Ground crews work in tandem with air ambulance crews, providing real-time information and guidance to facilitate safe and efficient landing zone operations.
7.3 Nighttime Landing Zone Lighting
Ground crews ensure proper lighting at landing zones to guide air ambulances during nighttime operations. This includes installing floodlights, portable lighting systems, or retro-reflective markers to clearly delineate the landing zone boundaries and any obstacles. Well-illuminated landing zones enhance the safety of both the air ambulance crews and the ground personnel, enabling smooth patient transfers and reducing the risk of accidents during takeoff and landing.
7.4 Communication Protocols with Ground Crew
Effective communication protocols between air and ground crews are critical for the success of nighttime operations. Ground crews provide essential information about landing zone conditions, obstacles, and patient status, allowing air ambulance crews to plan their approach and prioritize appropriate medical interventions. By establishing reliable communication channels and adhering to pre-defined protocols, air and ground crews ensure the seamless transfer of patients and maintain the safety and efficacy of nighttime air ambulance operations.
8. Challenges and Risks of Nighttime Operations
Conducting operations during nighttime poses unique challenges and risks for air ambulances. Understanding and mitigating these challenges is paramount for ensuring the safety and success of nighttime missions.
8.1 Limited Visibility
The most significant challenge of nighttime operations is the limitation of visibility. Darkness makes it difficult to identify hazards, such as wires, towers, or other aircraft. Air ambulance crews rely on advanced technology, night vision devices, and meticulously planned flight routes to overcome this challenge. However, even with these measures in place, crews must remain vigilant and maintain situational awareness to mitigate the risks associated with limited visibility.
8.2 Increased Fatigue Levels
Nighttime operations can induce increased fatigue levels in air ambulance crews due to the disruption of the natural sleep-wake cycle. Fatigue can impair decision-making, reaction times, and overall performance. To combat increased fatigue, air ambulance organizations implement strict work-hour restrictions, provide crew rest areas, and emphasize crew wellness initiatives. These measures help manage and mitigate the risks associated with fatigue during nighttime operations.
8.3 Unpredictable Weather Patterns
Nighttime weather patterns can be particularly unpredictable, posing risks to air ambulance operations. Rapidly changing weather conditions, such as fog, low clouds, or thunderstorms, require constant monitoring and timely decision-making. Flight crews receive continuous weather updates and collaborate with air traffic control to avoid adverse weather and ensure the safety of the patients and aircraft.
8.4 Enhanced Risk of Spatial Disorientation
Spatial disorientation is a significant risk during nighttime operations. In the absence of visual cues, flight crews may struggle to accurately perceive their aircraft’s altitude, position, and motion. Advanced instrumentation and flight planning techniques help mitigate the risk of spatial disorientation. Crews consistently cross-reference instrument readings, adhere to predetermined flight paths, and rely on their training to combat the challenges posed by spatial disorientation.

9. Safety Enhancements in Nighttime Operations
Air ambulance organizations prioritize safety enhancements to minimize risks during nighttime operations. These enhancements involve proactive measures such as safety audits, continuous training and evaluation, improved lighting technology, and adherence to regulations and standard operating procedures.
9.1 Nighttime Safety Audits
Regular safety audits in nighttime operations assess the effectiveness of procedures, equipment, and training protocols. Safety audits identify potential areas of improvement, ensuring that air ambulance organizations are up to date with the latest safety standards. By conducting comprehensive safety audits on a regular basis, organizations can proactively address any issues and enhance the safety of nighttime operations.
9.2 Continuous Training and Evaluation
Continuous training and evaluation programs are critical to maintaining high levels of proficiency in nighttime operations. Air ambulance crews undergo recurrent training sessions, including simulated scenarios, emergency drills, and night-specific training exercises. These programs allow crews to test their skills, learn from each experience, and continuously improve their readiness to handle nighttime emergencies.
9.3 Improved Lighting Technology
Advancements in lighting technology have greatly enhanced the safety of nighttime operations. Air ambulance organizations invest in state-of-the-art lighting systems that maximize visibility during critical phases of flight, such as takeoff, landing, and patient transfers. Improved lighting technology includes brighter exterior lights, increased helipad illumination, and customizable cabin lighting options. These advancements enhance crew visibility, reduce the risk of accidents, and improve overall patient safety.
9.4 Regulations and Standard Operating Procedures
Strict adherence to regulations and standard operating procedures is essential for safe nighttime operations. Regulatory bodies establish guidelines for air ambulance organizations, ensuring compliance with industry best practices. Standard operating procedures dictate specific protocols for various scenarios encountered during nighttime operations, leaving no room for ambiguity or error. By operating within a well-defined regulatory framework, air ambulance organizations maximize safety and maintain consistency across their nighttime operations.
10. Case Studies: Successful Nighttime Operations
Several case studies demonstrate the significant impact of nighttime operations in air ambulance services. These real-life examples exemplify the successful outcomes achieved through the dedicated efforts of air ambulance crews in navigating the darkness.
10.1 Critical Patient Transfer in Challenging Weather
In adverse weather conditions, air ambulances equipped for nighttime operations successfully transfer critically ill patients to specialized medical facilities. By leveraging night vision devices, advanced navigation systems, and continuous communication updates with ground crews and air traffic control, these missions effectively bridge the gap between patients and life-saving care, even in the most challenging weather.
10.2 Rescue from Remote and Dark Locations
Nighttime operations enable air ambulances to carry out rescue missions in remote and dark locations. These missions involve extracting stranded or injured individuals from areas inaccessible by ground transportation. Well-trained air ambulance crews leverage their expertise, advanced night vision devices, and collaborative ground crew coordination to safely navigate, locate, and evacuate those in need.
10.3 Dedicated Nighttime Air Ambulance Operations
Many air ambulance organizations run dedicated nighttime operations, recognizing the significant benefits of round-the-clock medical transportation. These operations require comprehensive training, the use of advanced technology, and adherence to stringent safety practices. Dedicated nighttime air ambulance operations ensure that critical patients receive the high-quality care they need, regardless of the time of day or level of darkness.
10.4 Improved Outcomes with Nighttime Operations
Numerous cases demonstrate improved patient outcomes as a result of nighttime air ambulance operations. Swift response times, efficient transportation, and access to specialized medical facilities during nighttime operations contribute to increased chances of survival and positive treatment outcomes. These successes underscore the critical role of air ambulances in providing life-saving care, regardless of the challenges imposed by darkness.
Nighttime Operations: How Air Ambulances Navigate in the Dark
Air ambulances play a vital role in providing urgent medical transportation, regardless of the time of day or environmental conditions. Nighttime operations offer enhanced accessibility, facilitate prompt responses to critical medical situations, reduce traffic congestion, and ensure efficient patient transportation. Through the use of advanced night vision devices, meticulous flight planning and instrumentation, effective communication with air traffic control, comprehensive crew training, and safety enhancements, air ambulances navigate the darkness with precision and care. The challenges and risks of nighttime operations are mitigated through continuous improvements, adherence to regulations and standard operating procedures, and proactive safety measures. Real-life case studies validate the immense impact of nighttime air ambulance operations, showcasing the successful outcomes achieved through the dedication and expertise of air ambulance crews. By embracing the unique demands of nighttime operations, air ambulance organizations save lives and make a significant difference in critical medical situations.